本文利用 GPS 的 GPRMC 消息及 PPS 信号,对多种传感器进行时间同步,涉及了不同的方法,总有一个适合你传感器的方法。
时间同步基础
gprmc 是 gps 所返回的一种国际标准信息,里面不仅带有经纬度欧拉角等信息,还带有当前的 utc 时间。但是数据的传输需要时间,往往所接收到的 gprmc 信息中的 utc 时间相比实际时间相差几百毫秒。而 pps 脉冲 ( 每秒一个脉冲 ) 精度非常高,可以达到几百毫秒,利用 pps 脉冲和 gprmc 中的 utc 时间,就可以精度校准系统的时间。
gps 信息回顾
本文方法理论上使用绝大多少 GPS。这里所使用的星网宇达 xw-gi5610,其带有 3 路 com, com0 rs232 接电脑,输出 gpfpd; com1 固定 422; com2 接 rtk,使 gps 接受 rtk 信号。另外有 5V 的 pps 脉冲,但是这个脉冲一般情况为高电平,触发时低电平,故使用的时候需要反相。
GPRMC+PPS 同步
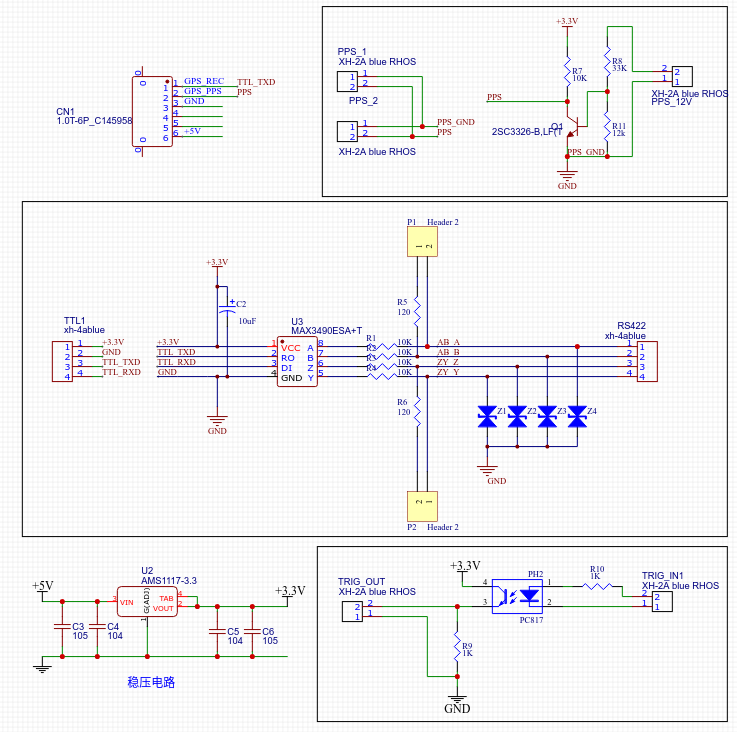
基于网络时间的同步
一些使用网络的传感器,如 Livox Horizon 雷达,不支持 GPRMC+PPS 同步,取而代之的是 PTP 网络同步协议 ( 或 NTP ) 。但是一般的 GPS 只有 GPRMC+PPS 的输出,为了实现 PTP 同步,这里使用一块 OrangePi Zero 读取 TTL 电平的 GPRMC 和 PPS 脉冲。
orangepi
尽管 orangepi zero ( 以下简称 zero ) 所使用的全志 H2 芯片内置了 rtc,但是 zero 没有引出 rtc 的供电引脚,因此在掉电之后,系统时间会停滞不前,这在我们的车辆环境上不可容忍。因此加装了一块 i2c 接口的 ds1307 模块,接线如下。
| 外设 | zero 引脚 | zero 引脚序号 |
|---|---|---|
| TXD | UART1_RX/PG06 | PIN10 |
| RXD | UART1_TX/PG07 | PIN8 |
| PPS | SIM_CLK/PA07 | PIN12 |
| SCK | TWI1-SCK/PA18 | PIN11 |
| SDA | TWI1-SDA/PA18 | PIN13 |
| VCC | 3.3V | PIN1 |
| GND | GND |
NTP 同步
随后使用 gpsd 读取 gps 数据,传入 chrony,使 orangepi zero 成为一个 ntp 时间服务器。
PTP 同步
另外由于 orangepi zero 的网卡支持软件 ptp 时间戳,所以使用 ptp4l 建立一个 ptp 主时钟。至此 orangepi 时间服务器建立完成。 除了传感器,工控机也可以使用 NTP 或 PTP 同步时间。比如 Livox 的雷达就支持 PTP 时间同步。
参考配置
注意本文所用的为orangepi zero,系统为 armbian。
rtc 配置
sudo armbian-config
- Select
Systemand click on OK - Click on
hardwareand click OK - turn on
i2c-0
/etc/default/hwclock
加上两句,配置 rtc1 为默认 rtc
HWCLOCKACCESS=yes
HCTOSYS_DEVICE=rtc1新建 /etc/systemd/system/ds1307.service 文件,内容如下
[Unit]
Description=ds1307 service
Before=hwclock.service chronyd.service
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/etc/ds1307.sh
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target新建 /etc/ds1307.sh 文件,内容如下
# !/bin/sh
echo "ds1307 0x68" > /sys/class/i2c-adapter/i2c-0/new_device
sleep 1
hwclock -s -f /dev/rtc1
hwclock --systohc -f /dev/rtc1
sleep 1赋予权限 sudo chmod +x /etc/ds1307.sh
重新加载服务 sudo systemctl daemon-reload
开机启动 sudo systemctl enable ds1307.service
gps 配置
sudo armbian-config
- Select
Systemand click on OK - Click on
hardwareand click OK - turn on
pps-gpioanduart1 - Click on
Edit Boot Environment( you can also edit this file directly/boot/armbianEnv.txt) - Add two lines to tell the Orange Pi Zero to use PA7 for PPS and uart1 for GPS NMEA messages
overlays=uart1 pps-gpio
param_pps_pin=PA7安装相关软件
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo apt-get remove ntp
sudo apt-get install chrony ptpd
sudo apt-get install pps-tools gpsd-clients之后插入 pps 和 gprmc,重启
检查 GPS 信号
sudo ppstest /dev/pps0
gpsmon /dev/ttyS1In order for NTPsec to recognise the GPS PPS combo we need to create some symlinks in /dev
sudo ln -sF /dev/ttyS1 /dev/gps1
sudo ln -sF /dev/pps0 /dev/gpspps1Create a new file in /etc/udev/rules.d called 99-gps.rules with the following:
KERNEL=="pps0",SYMLINK+="gpspps1",GROUP="dialout", MODE="0660"
KERNEL=="ttyS1", SYMLINK+="gps1",GROUP="dialout", MODE="0660"配置 chrony
/etc/chrony/chrony.conf
# This directive specify the location of the file containing ID/key pairs for
# NTP authentication.
keyfile /etc/chrony/chrony.keys
# This directive specify the file into which chronyd will store the rate
# information.
driftfile /var/lib/chrony/chrony.drift
# Uncomment the following line to turn logging on.
# log tracking measurements statistics
# Log files location.
logdir /var/log/chrony
# Stop bad estimates upsetting machine clock.
maxupdateskew 100.0
leapsectz right/UTC
makestep 1.0-1
# GPS 配置
refclock PPS /dev/gpspps1 lock GPSD prefer refid PPS
refclock SHM 0 offset 0.0 delay 0.2 refid GPSD
# 允许其他客户端连接
allow
# server 192.168.1.194 minpoll 2 maxpoll 4 polltarget 30 maxdelaydevratio 2 iburst
# leapsectz right/UTC
# makestep 1.0-1
# rtconutc
# rtcfile /var/lib/chrony/rtc
# rtcdevice /dev/rtc0
rtcdevice /dev/rtc1
hwclockfile /etc/adjtime
rtcautotrim 30
rtcsync修改 /etc/systemd/system/chronyd.service 文件,内容如下 ( 即设置让它在 ds1302 之后启动 )
[Unit]
Description=chrony, an NTP client/server
Documentation=man: chronyd ( 8 ) man: chronyc ( 1 ) man: chrony.conf ( 5 )
Conflicts=systemd-timesyncd.service openntpd.service ntp.service ntpsec.service
After=network.target ds1307.service
ConditionCapability=CAP_SYS_TIME
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/run/chronyd.pid
EnvironmentFile=-/etc/default/chrony
ExecStart=/usr/sbin/chronyd $DAEMON_OPTS
ExecStartPost=-/usr/lib/chrony/chrony-helper update-daemon
PrivateTmp=yes
ProtectHome=yes
ProtectSystem=full
[Install]
Alias=chronyd.service
WantedBy=multi-user.target重新加载服务 sudo systemctl daemon-reload
开机启动 sudo systemctl enable chronyd.service
配置 ptp
sudo apt install ptpd
# 删除默认的 ptpd.service ( 如果有 )
sudo rm /etc/systemd/system/ptpd.service新建 /etc/init.d/ptpd
以下为文件内容
# !/bin/sh
#
# /etc/init.d script for ptpd
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: ptpd
# Required-Start: $network $remote_fs
# Required-Stop: $network $remote_fs
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: start and stop ptpd
# Description: ptpd is the Precision Time Protocol daemon ( IEEE1588-2008 )
### END INIT INFO
PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin
DESC="Precision Time Protocol daemon"
NAME=ptpd
DAEMON=/usr/sbin/$NAME
PIDFILE=/var/run/ptpd2.lock
SCRIPTNAME=/etc/init.d/$NAME
# Exit if the package is not installed
[ -x "$DAEMON" ] || exit 0
case $1 in
start )
a=$ ( ip addr show to 192.168.1.194/16 | wc -l )
until [ "$a" -gt 0 ]
do
a=$ ( ip addr show to 192.168.1.194/16 | wc -l )
echo Sleeping
sleep 1
done
#What it does:
#print all address of ipv4 interfaces | filter out the link-local address ( es ) | substitute all the remaining information except for the ': if-name ' part. | strip the leading ': ' and trailing ' '.
#Lastly, the $ ( ... ) is called 'command substution' which in this case dumps the output into the variable IF_NAME.
IF_NAME=$ ( ip -o -4 addr | grep -e 192.\168 | sed -n 's/.*\ ( : [a-zA-Z0-9]* \ ) .*/\1/ p' | sed -n 's/: \ ( [a-zA-Z0-9]*\ ) /\1/ p' )
start-stop-daemon --start --quiet --pidfile $PIDFILE --exec $DAEMON -v -- -i $IF_NAME -M \
|| return 0
;;
stop )
start-stop-daemon --stop --quiet --retry=TERM/30/KILL/5 --pidfile $PIDFILE --name $NAME
;;
- )
echo "Usage: {start|stop}"
;;
esac随后更新
sudo update-rc.d ptpd start 98 2 3 4 5 . stop 2 0 1 6
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable ptpd
sudo systemctl restart ptpd